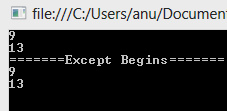
In the Last blog we saw how to find the uncommon things in particular list.
http://linqdetails.blogspot.in/2014/07/llinq-except.html
Now we need to find the uncommon things in both the list. We will continue with same example. First we will start with simple integer type , then we will go for class.
It works for
List<int> uncommonBoth = num1.Concat(num2).Except(CommoninNum1Num2).ToList();
So what is the difference between Concat and Union ???
I have explained here.
http://linqdetails.blogspot.com/2014/07/difference-between-concat-and-union.html
================================================================
-------------------Now we want both the things---------------------------------------------------------------
Biswa 1
Prasad 3
Abhi 1
Siba 3
-- This gives me both the resullts.
-- We can use Concat too
-- You need to use dynamic otherwise you will get error. items will be resolved at runtime whether its from list1 or list2. if from list1 then at runtime the firstname will be resolved as of list1.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
http://linqdetails.blogspot.in/2014/07/llinq-except.html
Now we need to find the uncommon things in both the list. We will continue with same example. First we will start with simple integer type , then we will go for class.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> num1 = new List<int> { 1, 4, 7, 12 };
List<int> num2 = new List<int> { 1, 9, 7, 13, 13 };
List<int> num2NotinNum1 = num2.Where(x => !num1.Contains(x)).Distinct().ToList();// 4 12
List<int> num1NotinNum2 = num1.Where(x => !num2.Contains(x)).Distinct().ToList(); //9 13
List<int> CommoninNum1Num2 = num1.Intersect(num2).ToList(); // 1 7
List<int> uncommonBoth = num1.Union(num2).Except(CommoninNum1Num2).ToList();
foreach (int uncommon in uncommonBoth)
{
Console.WriteLine(uncommon);
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
} It works for
List<int> uncommonBoth = num1.Concat(num2).Except(CommoninNum1Num2).ToList();
So what is the difference between Concat and Union ???
I have explained here.
http://linqdetails.blogspot.com/2014/07/difference-between-concat-and-union.html
================================================================
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
class list1
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string Id { get; set; }
}
class list2
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string Id { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<list1> list1 = new List<list1>();
List<list2> list2 = new List<list2>();
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "1" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "2" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Prasad", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Abhi", Id = "1" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "2" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Siba", Id = "3" });
List<list1> list1NotInList2 = list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList();
List<list2> list2NotInList1 = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList();
Console.WriteLine("====Items in LIst1 but Not in list2===========");
foreach (list1 items in list1NotInList2)
{
Console.WriteLine(items.FirstName + " " + items.Id);
}
Console.WriteLine("====Items in LIst2 but Not in list1============");
foreach (list2 items in list2NotInList1)
{
Console.WriteLine(items.FirstName + " " + items.Id);
}
}
} -------------------Now we want both the things---------------------------------------------------------------
var finalcommonresult = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList().Cast<object>().Union
(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList().Cast<object>());
foreach (dynamic items in finalcommonresult)
{
Console.WriteLine(items.FirstName + " " + items.Id);
} Biswa 1
Prasad 3
Abhi 1
Siba 3
-- This gives me both the resullts.
-- We can use Concat too
-- You need to use dynamic otherwise you will get error. items will be resolved at runtime whether its from list1 or list2. if from list1 then at runtime the firstname will be resolved as of list1.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "1" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "7" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Abhi", Id = "1" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "2" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Siba", Id = "3" });
var finalcommonresult = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x=>x.FirstName).ToList().Cast<object>()
.Union(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x => x.FirstName).ToList().Cast<object>());
Here we get
Abhi
Siba
Biswa
The same thing with concat will give
var finalcommonresult = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x=>x.FirstName).ToList().Cast<object>()
.Concat(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList()
.Select(x=>x.FirstName).Cast<object>());
Abhi
Siba
Biswa
Biswa
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "1" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "7" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "1" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Abhi", Id = "1" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "2" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Siba", Id = "3" });
var finalcommonresult = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.ToList().Cast<object>().Union(list1.Where(x => !list2
.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).ToList().Cast<object>());
Here we get
Abhi 1
Siba 3
Biswa 1
Biswa 1
If we are not selecting anything even if both same the records [Biswa 1 and Biswa 1] are same, union gives all the results.
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
So lets try selecting both the items. Earlier we have selected First Name. Now to select both items use anonymous type. Use the new keyword followed by curly braces.
var finalcommonresult = list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select( x=> new { x.FirstName,x.Id}).ToList().Cast<object>()
.Union(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x => new { x.FirstName, x.Id }).ToList().Cast<object>());
Abhi 1
Siba 3
Biswa 1
Cool :)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "1" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "7" });
list1.Add(new list1 { FirstName = "Biswa", Id = "9" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Abhi", Id = "1" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "2" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Anurag", Id = "3" });
list2.Add(new list2 { FirstName = "Siba", Id = "3" });
var finalcommonresult = list2
.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select( x=> new { x.FirstName,x.Id}).ToList().Cast<object>()
.Union(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName)).Select(x => new { x.FirstName, x.Id }).ToList().Cast<object>());
Abhi 1
Siba 3
Biswa 1
Biswa 9
ok cool :)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You can also use Distinct for above queries.
Distinct also works when we are filtering on anonymous types.
var distinctlist1 = list1.Select(x=> new {x.FirstName,x.Id}).ToList().Distinct(); // this will give distinct
var distinctlist11 = list1.ToList().Distinct();//this will not give distinct
So we can use Distinct + Concat. Because Distinct + Union will not make any sense as Union will take the distinct if we are working on anonymous types.
var finalcommonresult =
list2.Where(x => !list1.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x=> new {x.FirstName,x.Id}).ToList().Distinct().Cast<object>()
.Concat(list1.Where(x => !list2.Any(y => y.FirstName == x.FirstName))
.Select(x => new { x.FirstName, x.Id }).ToList().Distinct().Cast<object>());
To select a distinct you need to do as anonymous type too.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------